Oral and Dental Health During Pregnancy
Oral and dental health during pregnancy; It is necessary to evaluate it in three time periods: before pregnancy, during pregnancy and after pregnancy. There are different approaches and common behaviors in these three different periods.

-
The Importance of Oral and Dental Health During Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a special time when significant changes occur in oral and dental health, as in many other systems in the body. Dental health during pregnancy can directly impact not only the mother's health but also the baby's. Therefore, it is extremely important to prioritize dental health during pregnancy.
Increased hormone levels during pregnancy, particularly estrogen and progesterone, can lead to problems such as gingivitis (pregnancy gingivitis). Swollen, bleeding, and tender gums are often observed during pregnancy. Furthermore, hormonal changes can cause sensitivity due to gum problems, and harmful bacteria can accumulate in the mouth, increasing the risk of cavities. Regular dental checkups should not be neglected during this period. Furthermore, expectant mothers should maintain regular and adequate oral and dental care.
It is important to remember that dental disease during pregnancy can negatively impact the health of both mother and baby.
-
Factors Affecting Oral and Dental Health During Pregnancy
Many factors affect oral and dental health during pregnancy. Hormonal and immune system changes during pregnancy can trigger certain gum diseases. This often manifests as inflammation and bleeding of the gums (pregnancy gingivitis). Changes in eating habits during pregnancy, such as cravings, can also have some impacts on dental health, as individuals may overconsume acidic, sour, and sweet foods during pregnancy. Additionally, nausea and vomiting, especially during the first trimester, can cause the oral environment to become acidic. This can disrupt the salivary balance in the mouth, weakening tooth enamel and increasing the risk of cavities. Considering all these factors, oral health during pregnancy can become more sensitive and vulnerable than usual, so routine dental checkups and regular oral hygiene are crucial.
-
Toothache During Pregnancy
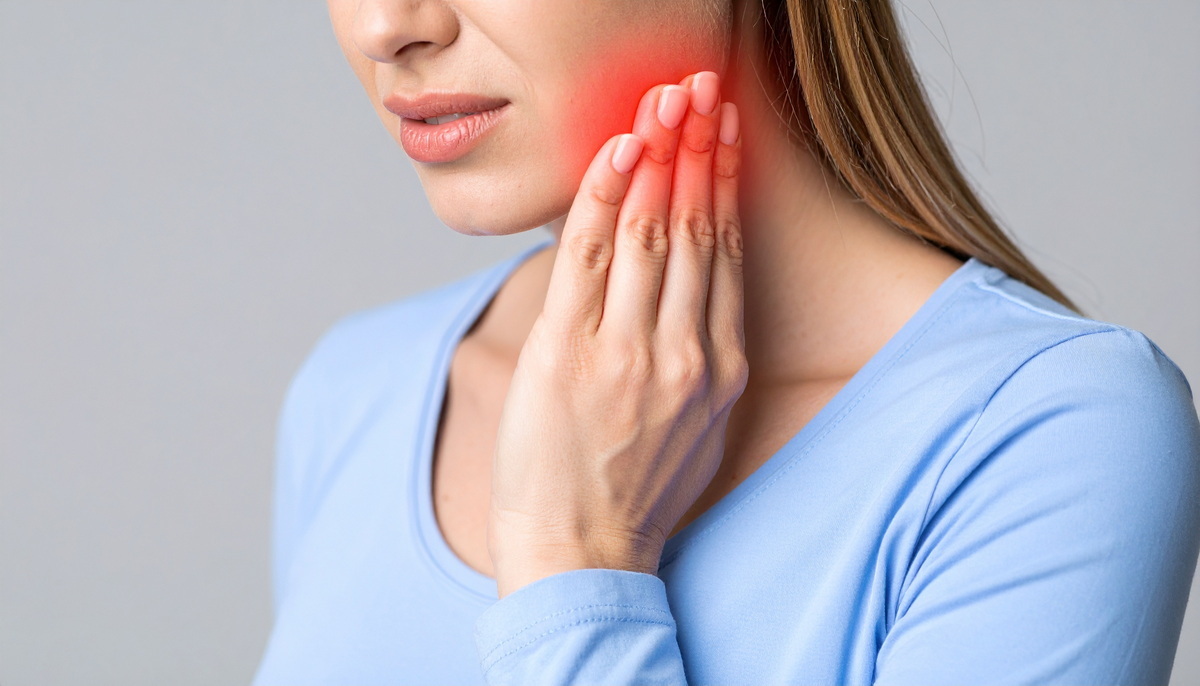
If you experience toothache during pregnancy, the cause should be evaluated by a dentist. There is a common misconception that dental treatment is not possible during pregnancy, so expectant mothers often choose to postpone treatment in cases of toothache. Toothaches can develop for many reasons and may be a sign of advancing decay or various gum diseases. Early intervention can help the dentist manage the condition and help the expectant mother have a comfortable pregnancy.
-
How to Relieve Toothaches During Pregnancy?
Some natural home remedies, such as gargling with salt water and using cold compresses, can provide temporary relief, but the solution isn't permanent. Some painkillers can relieve toothaches with a doctor's approval, but to completely relieve and treat the pain, the condition must be evaluated by a specialist dentist. Treating a painful tooth during pregnancy will provide the most lasting and safe results. There's no harm in pregnant women experiencing a toothache and seeking treatment from a dentist. At Jimer Dental Clinics, our dentists, with over 15 years of experience, carefully evaluate this delicate condition in pregnancy and provide the safest treatment for both mother and baby. You can find detailed information about our specialist dentists by clicking here.
-
Gum Disease During Pregnancy (Pregnancy Gingivitis)
Gingivitis during pregnancy is a very common gum problem during pregnancy. It is usually associated with hormonal changes in the second and third trimesters. Bleeding gums during pregnancy are often caused by increased progesterone and estrogen levels. Blood circulation in the gums also changes, leading to swelling, bleeding, and tenderness. For example, expectant mothers may experience irritation and pain when performing routine dental care with toothbrushing and flossing. This can make oral care during pregnancy challenging. Furthermore, changes in the immune system during pregnancy can make gums more susceptible to bacteria. Pregnant women with poor oral hygiene and gum inflammation are also at risk of developing pregnancy-related tumors. These are gum growths that usually disappear after birth. However, if they interfere with dental care or cause discomfort, they should be examined by a specialist dentist. Professional scaling and routine checkups performed by a dentist can help rule out potential gum disease.
-
Is Dental Treatment Safe During Pregnancy?
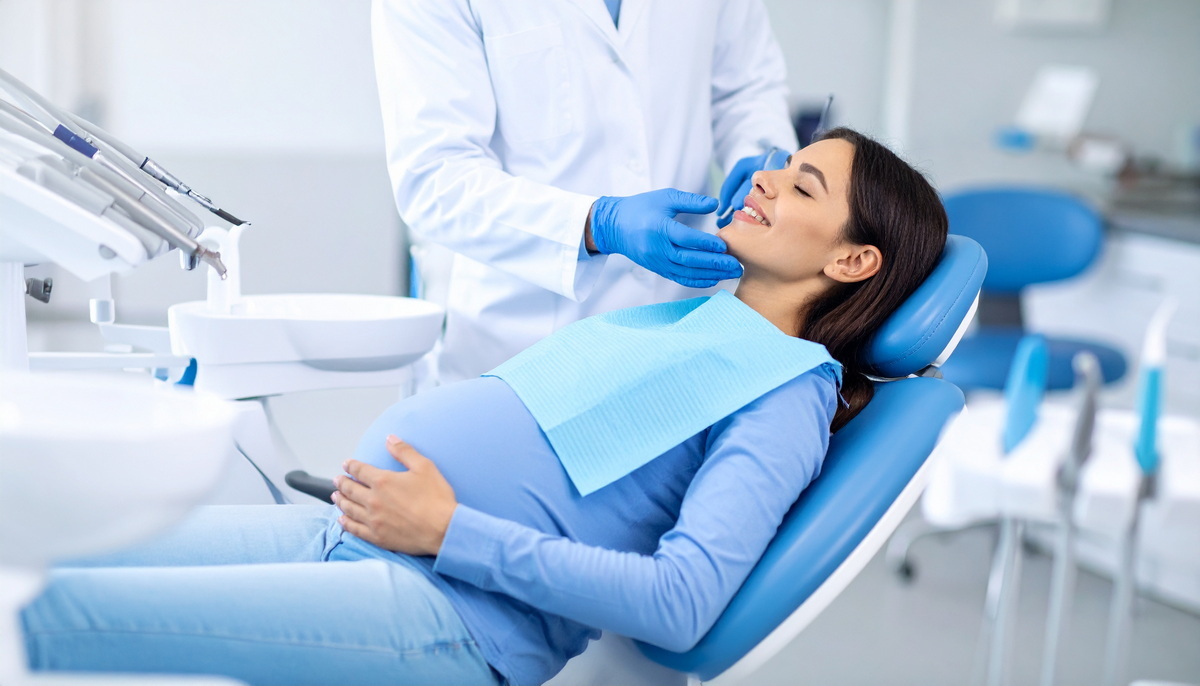
Having dental treatment during pregnancy is extremely safe and does not cause any health problems for the mother or baby. Expectant mothers can safely receive treatment by providing the dentist with the necessary information about their pregnancy and general health. Local anesthetics and treatment materials used in dental treatment have no harmful effects on the health of the mother or baby. Unless there is an emergency, the dentist may choose to postpone treatment until a certain point in the pregnancy. In cases of severe pain or requiring urgent intervention, they may schedule immediate treatment without delay. The second trimester (middle trimester) is generally the preferred time for dental treatment.
-
What are Safe Dental Treatments During Pregnancy?
Dental cleanings can be performed during pregnancy.
Depending on the severity of tooth decay, your dentist may recommend regular checkups. In cases of emergency tooth decay, fillings and root canal treatment can be performed as needed, based on the dentist's plan.
Procedures such as tooth extractions are generally preferred during the middle trimester (between 3-6 months). Your dentist will develop the most appropriate plan for you based on your current pregnancy and overall oral and dental health.
-
Is Dental X-Ray Harmful During Pregnancy?

The modern, state-of-the-art dental X-ray and CT scan devices at our clinic emit very low levels of radiation, so the risk of harming an unborn baby is low. However, unless there are emergencies, radiologic evaluations are generally postponed if the patient is in the first trimester of pregnancy, as this is the most sensitive period for fetal development. In emergencies such as severe pain or infection, and if an X-ray is necessary, the pregnant woman is asked to wear a lead apron and goggles. X-rays are administered at low doses.
-
Dental Treatments During Pregnancy, Bursa
At our Jimer Dental Clinics in Nilüfer Parkora and our dental clinic within the hospital, we provide all dental treatments safely for pregnant women. Our dentists have extensive experience in the oral health and dental treatment of pregnant women. If you are looking for a clinic in Bursa that offers dental treatment for pregnant women, please contact us at +90 533 738 14 52 to learn more about the process.
-
Dental Treatment Planning During Pregnancy

Dental treatment planning during pregnancy varies depending on many factors, including the pregnant woman's general health, the trimester of pregnancy, and the urgency of the treatment. Dental treatments during pregnancy are generally planned by a dentist, considering the health of both mother and baby, as follows:
- Pre-Pregnancy Planning: Before planning a pregnancy, routine dental checkups should be conducted with a dentist, and any necessary treatments should be completed. If severe dental problems arise during pregnancy, the patient should consult her doctor and then be examined by a dentist.
- Second Trimester The 14th to 26th weeks of pregnancy are a period when the baby's basic development is largely complete and the mother adapts more easily to the pregnancy. Therefore, this period is generally the most appropriate and safest time for dental treatments. For non-urgent dental treatments, treatment can be postponed for a while by monitoring the pregnant woman with routine checkups.
- Conditions Requiring Urgent Treatment: If you have a dental problem requiring urgent intervention (such as a severe toothache, a tooth abscess, or gingivitis), treatment should be initiated immediately.
- Routine Dental Treatments: Routine dental treatments (e.g., scaling, dental fillings, root canal treatment, or simple tooth extraction) are generally safe and can be performed during pregnancy.
- Use of Radiography: X-rays or dental CT scans may be necessary when deemed necessary by the dentist. In such cases, protective measures such as a lead apron and low-dose application are taken, and the x-rays are taken with minimal risk.
- Prolonged Delay of Treatment: Some dental treatments may need to be postponed during pregnancy, especially for more serious surgical procedures (such as implants) and other treatments requiring the use of medications.
-
Misconceptions About Dental Health During Pregnancy
-
-Dental treatment during pregnancy is harmful: FALSE
Routine dental visits and completion of necessary treatments before planning a pregnancy are recommended to prevent potential problems. However, dental treatment can be safely performed during pregnancy. Only in the first trimester of pregnancy, if the dentist deems it appropriate, treatment can be postponed for a while in non-urgent situations. However, in emergencies, dental treatment can be performed at any stage of pregnancy. The notion that dental treatment will harm the mother and baby is a misconception. Dental treatment performed with the necessary precautions and appropriate treatment planning is extremely safe.
-
-Calcium does not dissolve from teeth during pregnancy: TRUE
If the expectant mother cannot meet her calcium needs from food, the calcium necessary for the baby's development can be obtained from the mother's bones, but calcium is not absorbed from the teeth.
-
-Teeth should be brushed less frequently during pregnancy: FALSE
Expectant mothers whose gums bleed during pregnancy due to the effects of pregnancy hormones may avoid brushing their teeth for fear of further bleeding. During pregnancy, individuals experiencing bleeding gums should brush their teeth regularly and maintain good oral hygiene. Teeth should be brushed regularly at least twice a day. Furthermore, expectant mothers experiencing bleeding gums should be examined by a dentist to prevent potential problems.
-
-Scaling (plaque) should not be done during pregnancy: FALSE
Due to the hormonal surge during pregnancy, the oral environment can become more susceptible and sensitive to external factors, especially bacteria. Therefore, scaling during pregnancy is an effective solution to maintain the challenging task of maintaining oral hygiene. Scaling not only soothes the gums but also improves existing gum disease. No medications are used during the cleaning process, which could jeopardize the health of the mother or baby; it is an extremely safe and beneficial procedure.
-
-Every Pregnancy Causes Tooth Loss: FALSE
There is a misconception in society that pregnancy negatively affects dental health and leads to tooth loss. Many people claim that the unborn baby reduces the mother's calcium intake, which she then takes from her teeth and bones. However, this isn't entirely true; calcium needs aren't met by teeth. While some changes can affect oral and dental health during pregnancy, contrary to popular belief, these changes don't lead to tooth loss. Regular oral hygiene and routine dental checkups during pregnancy largely prevent the risk of tooth loss.
-
-
Oral Care During Pregnancy
Oral hygiene should be maintained throughout pregnancy with regular brushing and flossing. Teeth should be brushed at least twice a day, and if possible, after every meal. The spaces between teeth should be cleaned with dental floss. Pregnant women experiencing bleeding gums should not stop brushing and flossing for fear of further bleeding; they should continue to do so regularly.
-
Nutrition for Dental Health During Pregnancy
Good nutrition during pregnancy will positively impact the dental health of both mother and baby. Baby's tooth development begins in the second month of pregnancy. Consuming foods rich in calcium, vitamin D, and phosphorus is recommended for healthy tooth development. Expectant mothers should limit sugar intake starting in the first month of pregnancy, avoid junk foods like crackers and cookies, which can easily stick to teeth, and avoid acidic beverages whenever possible.
In conclusion, maintaining oral and dental health is crucial for the overall health of both mother and baby. If you would like to learn more about dental treatment during pregnancy and schedule an appointment, please contact our expert team for detailed information.
Dental treatments are safe, especially during the second trimester of pregnancy (weeks 13-27). However, it's always important to consult your dentist and obstetrician.
You should always consult your doctor about medication use during pregnancy. Pain relievers containing paracetamol are generally recommended, but dosage and duration of use should be monitored by a doctor.
Yes, tooth extractions can be performed in emergency situations, especially during the second trimester. Local anesthesia is generally safe, but a doctor's approval is required in all cases.
With modern digital X-ray equipment and appropriate protective measures (such as using a lead apron and administering low doses), dental X-rays are safe. Dentists should avoid X-rays unless absolutely necessary. Unnecessary X-rays should be avoided.
Hormonal changes can cause sensitive and bleeding gums. However, this can be a sign of gum disease, so it's important to consult a dentist.
Having dental treatment during pregnancy is safe and poses no risk to the health of the mother or baby. Dental treatment is carried out with the appropriate planning by the dentist, taking into account the health of both mother and baby.
People experiencing toothaches during pregnancy should consult a dentist. Home remedies or painkillers are only temporary solutions. A dental visit is necessary for a permanent solution.
Simple tooth extractions can be safely performed during pregnancy, but more complex extractions may require surgery. In such cases, the pregnant woman may need to consult her doctor, and surgical extractions can be performed with a special plan when appropriate.
All general dental treatments (fillings, root canals, tooth extractions, tartar removal, etc.) can be safely performed during pregnancy with a personalized plan.
Dental treatment can usually be postponed for a while during the first trimester, unless there's an emergency. However, a dentist should still examine and guide the patient. If dental treatments aren't monitored and treated, they can lead to serious problems in the future and negatively impact both mother and baby.
Expectant mothers should brush and floss twice a day, morning and evening.
Anne adayları bebeğin diş ve kemik gelişimi için kalsiyum, fosfor ve diğer mineraller açısından zengin besinler tüketmelidir.
Expectant mothers should consume foods rich in calcium, phosphorus, and other minerals to support their babies' teeth and bone development.
Hormonal changes during pregnancy, vomiting, or food cravings can alter the environment in the mouth, leading to bad breath.
Regular oral care during pregnancy is crucial for maintaining oral and dental health. Brushing with fluoride toothpaste and flossing at least twice a day is essential to prevent potential dental problems.
Take advantage of our Oral and Dental Health During Pregnancy service now!
Complete the form to receive complimentary 5 star hotel, spa services, breakfast, and vip transfer.
Our Specialists

Dt. Ömer Demirçak
Dentist
Spc. Dt. Zeynep Ovalıoğlu
Endodontics (Root Treatment) Specialist
 TR
TR DE
DE